GRX-Q - Flow measurement
The flow measurement is part of the metrological determination of a volume flow Q or mass flow m=ρ∙Q. This is done as a function of a measuring cross-section A of a closed pipe or an open channel.
Flow measurement can be carried out on any fluids, such as cooling lubricants, and is used in a wide variety of areas. Depending on the measuring and evaluation method, flow meters are used in power and work machines, disposal technology, process engineering, chemical production processes and air conditioning and ventilation technology. Another area is the monitoring, control and regulation of coolant and lubricant circuits on CNC machines for machining, for example.
A distinction is made between two measuring methods. On the one hand, there are direct measuring methods, in which only a single measured variable is required to determine the flow rate. On the other hand, there are indirect measuring methods in which one or more additional variables must be known or measured in addition to the main measured variable.

Overview: Flow meters and how they work
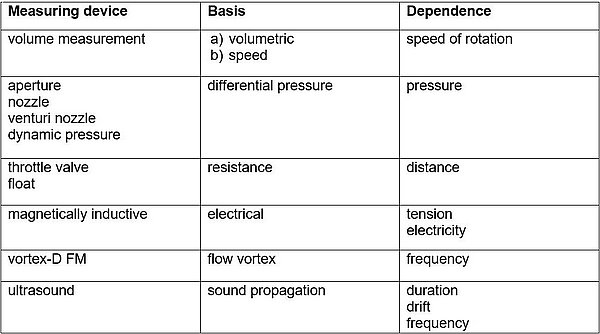
Flow and volume measuring devices can be divided into two main groups. The first main group consists of flow meters for open channels, while the second main group consists of flow and volume meters for closed pipelines.
In this paper, only measuring devices for closed pipes are considered and described below.
In particular, the flow meters (DFM) relevant for a grinding process are discussed.
An overview of the sensors is listed in Table 2-4.
Products relevant to this article:
GRX-Q

You may also be interested in these articles from our magazine:
Cooling during grinding
![[Translate to Englisch:] Kühlen beim Schleifen [Translate to Englisch:] Warum Schleifen und Kühlen zusammengehören](https://grindaix.de/fileadmin/_processed_/b/a/csm_iStock_000011384066XSmall_dd136b394c.jpg)
A great deal of heat is generated during grinding due to process-related friction. This heat must be reliably dissipated, which is why grinding processes require reliable cooling. You can read about what is important here.
GRX-Q - Volumetric measuring method
The volumetric measuring method is based on the measurement of partial quantities of a medium to be measured. The medium flowing through a defined measuring chamber or via an analog rotation of measuring vanes is added up.
GRX-Q - Magnetic-inductive flow measurement
In magnetic-inductive flow measurement (MID), an electrical voltage is generated by the interaction between the flow velocity of a liquid and a magnetic field. This principle is based on Faraday's law of induction.



